Inactive ingredients in generic medications can interact when taken together, causing side effects like stomach upset, rashes, or reduced drug effectiveness. Learn how to spot risky excipients and protect yourself.
Category: Medications - Page 2
Switching warfarin generics can affect your INR and increase bleeding or clotting risks. Learn when and how to monitor safely, what causes instability, and why cost savings shouldn't compromise safety.
Learn how to read FDA-required Medication Guides to spot serious risks and monitoring requirements for your prescription drugs. Know what to look for, when to act, and how to stay safe.
Provider Education on Generics: How Clinicians Can Improve Patient Outcomes with Generic Medications
Provider education on generics improves clinician confidence, reduces patient costs, and boosts adherence. Learn how FDA standards, communication strategies, and EHR tools are closing the knowledge gap in generic prescribing.
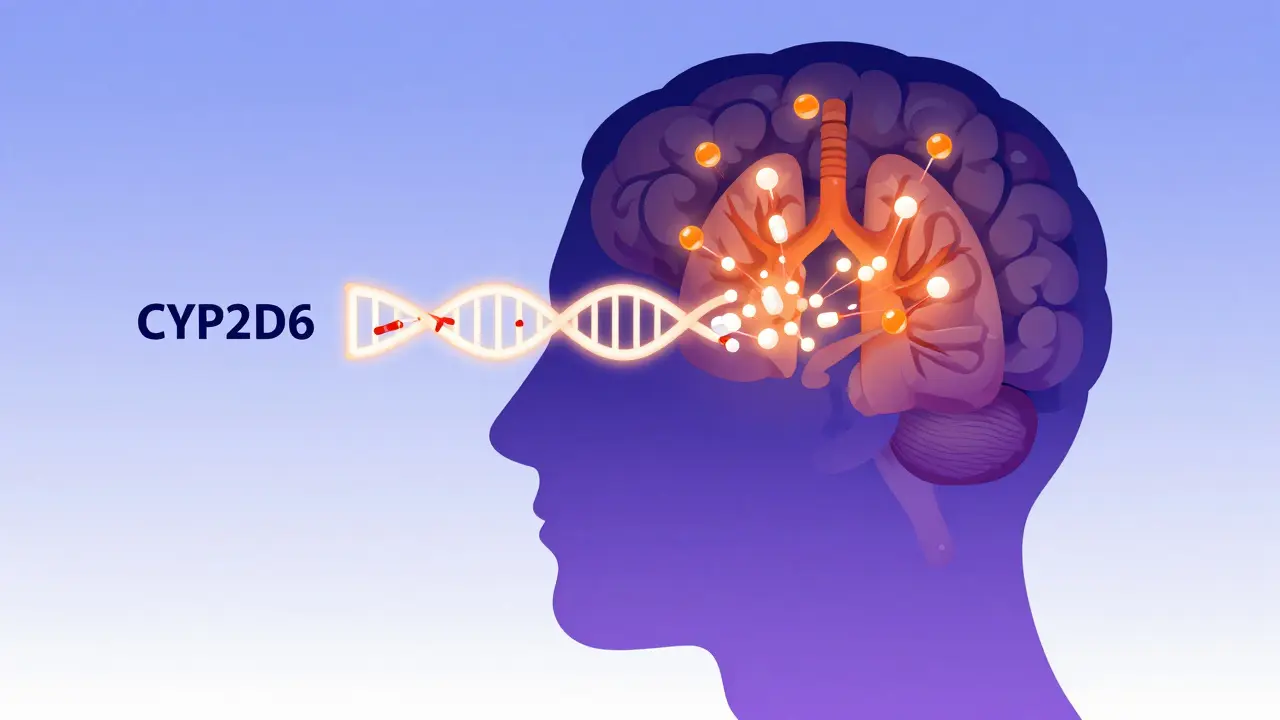
Codeine can be deadly for people with a genetic trait called CYP2D6 ultrarapid metabolism. Even standard doses can cause fatal overdose by turning too quickly into morphine. Learn who's at risk and what safer alternatives exist.
Learn how insurance formularies treat generic vs brand-name drugs, what you really pay, when substitutions happen, and how to fight for the right medication if generics don't work for you.
Naloxone can reverse opioid overdoses in minutes - if you know how to use it. Learn how to recognize signs of overdose, administer naloxone safely, store it properly, and why calling 911 is always necessary.
Generic prescribing incentives reward doctors for choosing lower-cost generic drugs, saving billions in healthcare spending. But how do these programs really work-and when do they risk compromising care?
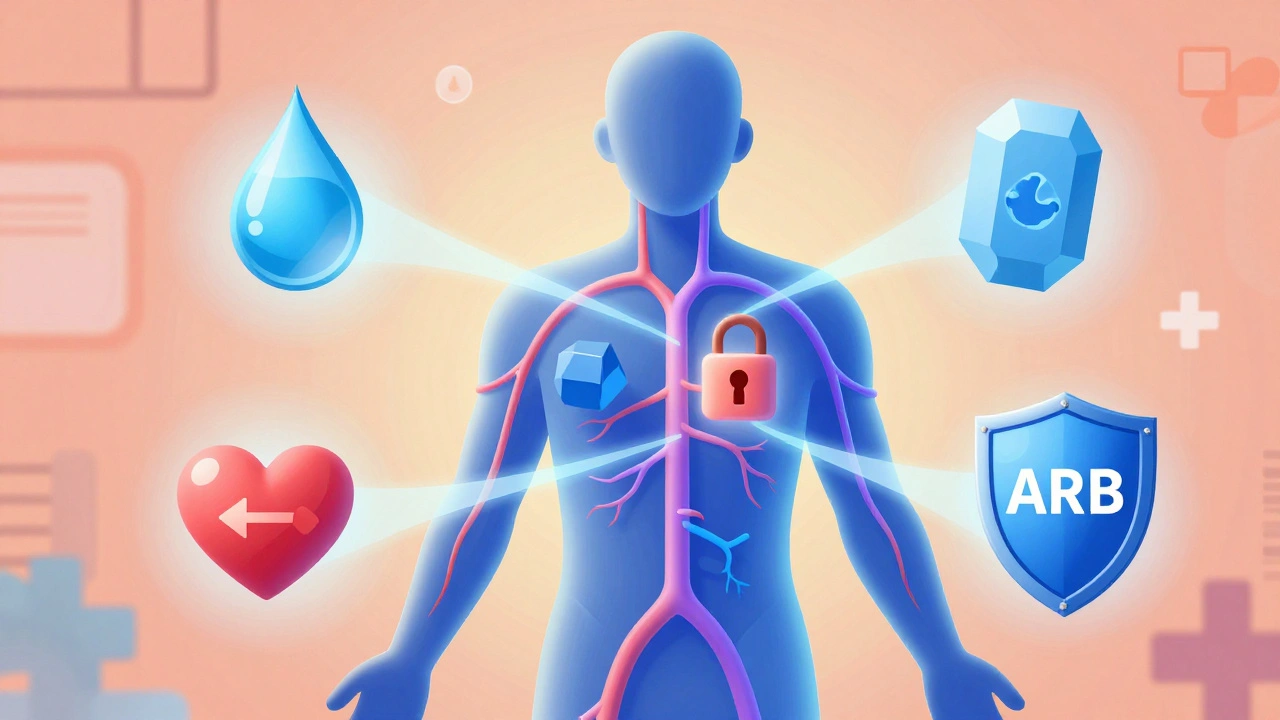
Learn the five main types of blood pressure medications, their common side effects, dangerous interactions, and how doctors choose the safest option for you based on your health profile in 2025.
Therapeutic interchange means swapping medications within the same class to cut costs without losing effectiveness. It’s not a random change - it’s a structured, evidence-based practice used mostly in hospitals and nursing homes.