The Connection Between Schizophrenia and Autoimmune Disorders

Introduction: Schizophrenia and Autoimmune Disorders
Schizophrenia is a severe and chronic mental disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. It is characterized by a range of symptoms, including hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech, and impaired cognitive abilities. Autoimmune disorders, on the other hand, occur when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues and organs. Over the years, researchers have been investigating the connection between schizophrenia and autoimmune disorders. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of this connection and discuss the latest findings.
The Role of Inflammation in Schizophrenia and Autoimmune Disorders
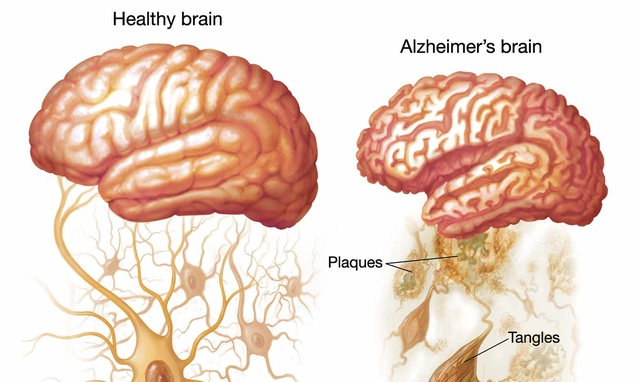
One of the key factors linking schizophrenia and autoimmune disorders is inflammation. Inflammation is a natural response of the body's immune system to harmful stimuli, such as injury or infection. However, when inflammation becomes chronic, it can lead to various health problems, including autoimmune diseases and mental disorders like schizophrenia.
Studies have shown that individuals with schizophrenia often exhibit increased levels of inflammation markers, such as cytokines and C-reactive protein (CRP). This suggests that inflammation may play a role in the development or progression of the disorder. Similarly, autoimmune disorders are characterized by chronic inflammation, resulting from the immune system's overreaction to its own tissues.
Genetic Links Between Schizophrenia and Autoimmune Disorders
Recent research has also revealed possible genetic connections between schizophrenia and autoimmune disorders. Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified several genes that are associated with an increased risk of developing both schizophrenia and various autoimmune diseases. For example, the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) region on chromosome 6 has been found to play a role in the development of both schizophrenia and autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis.
These shared genetic factors suggest that there might be common biological pathways underlying both schizophrenia and autoimmune diseases, which could help explain the connection between the two conditions.
Environmental Triggers and Epigenetics
Environmental factors can also contribute to the development of both schizophrenia and autoimmune disorders. For instance, infections, particularly during early life or prenatal period, have been linked to an increased risk of schizophrenia. These infections can cause inflammation and activate the immune system, which could then lead to the development of autoimmune disorders.
Epigenetics, the study of how environmental factors can alter gene expression without changing the DNA sequence, has also emerged as an important factor in understanding the connection between schizophrenia and autoimmune disorders. Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone modification, can be influenced by various environmental factors, including infections, stress, and nutrition. These modifications can then affect the expression of genes involved in immune system regulation and inflammatory processes, possibly contributing to the development of both schizophrenia and autoimmune diseases.
Autoimmune Disorders as Risk Factors for Schizophrenia
There is evidence to suggest that individuals with certain autoimmune disorders may be at an increased risk of developing schizophrenia. For example, studies have shown that people with celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder affecting the small intestine, have a higher risk of schizophrenia compared to the general population. Similarly, individuals with autoimmune thyroid disorders have been found to be at an increased risk of developing schizophrenia.
The exact mechanisms behind this increased risk are not yet fully understood, but it is thought that the chronic inflammation associated with autoimmune disorders may contribute to the development of schizophrenia by affecting the brain and its functions.
Treatment Implications: Targeting Inflammation and Immune Dysregulation
Understanding the connection between schizophrenia and autoimmune disorders has important implications for the treatment of both conditions. Since inflammation and immune dysregulation appear to play a crucial role in the development of schizophrenia and autoimmune diseases, targeting these processes could potentially improve treatment outcomes for patients with these conditions.
For example, anti-inflammatory medications, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids, have shown promise in reducing symptoms in some patients with schizophrenia. Similarly, immunomodulatory therapies, which aim to regulate the immune system's activity, are currently being investigated as potential treatments for both schizophrenia and autoimmune disorders.
Conclusion: The Complex Connection Between Schizophrenia and Autoimmune Disorders
The connection between schizophrenia and autoimmune disorders is complex and multifaceted, involving genetic, environmental, and immunological factors. Understanding this connection can help researchers develop more effective treatments for both conditions, as well as shed light on the underlying biological mechanisms that contribute to their development. While more research is needed to fully elucidate the connection between schizophrenia and autoimmune disorders, the current evidence suggests that inflammation and immune dysregulation may be key factors linking these two seemingly disparate conditions.


Dheeraj Mehta
Interesting read, glad research is moving forward! :)
Oliver Behr
The inflammation link makes a lot of sense, especially given the cytokine spikes seen in both conditions.
Tiffany W
One must consider the immunopathogenic axis, whereby the upregulation of IL‑6 and TNF‑α orchestrates neuroinflammatory cascades, thereby potentiating psychotic phenotypes.
Rajeshwar N.
I’m skeptical that correlation implies causation; many of these studies suffer from confounding lifestyle variables.
Louis Antonio
Actually, the data from longitudinal cohorts control for smoking and BMI, so the association persists beyond simple confounds.
Kyle Salisbury
From a South Asian perspective, dietary patterns and gut microbiota could modulate immune responses, adding another layer to the schizophrenia-autoimmunity puzzle.
Angie Robinson
But the microbiome argument is overhyped; most of the evidence is correlative and lacks mechanistic depth.
Emmons Kimery
Great synthesis! It’s encouraging to see multidisciplinary approaches gaining traction. 🌍🙂
Mimi Saki
Absolutely, bridging neurology and immunology can only benefit patients 🙌😊
Subramaniam Sankaranarayanan
The genetic overlap between schizophrenia and autoimmune conditions is striking, especially with the MHC locus emerging as a shared risk hotspot. Recent GWAS have identified dozens of SNPs that confer susceptibility to both disease families, suggesting a convergent evolutionary pressure on immune regulation pathways. Epigenetic modifications further complicate the picture; prenatal infections can leave lasting methylation marks that alter cytokine production later in life. Environmental triggers such as urban stressors and vitamin D deficiency may act synergistically with these genetic predispositions, fueling chronic inflammation. Moreover, the blood‑brain barrier’s permeability appears to increase under sustained peripheral immune activation, allowing autoantibodies to affect neural circuitry. Clinical observations of heightened CRP levels in psychotic episodes reinforce the notion of a systemic inflammatory milieu. Therapeutically, anti‑inflammatory agents like celecoxib have shown modest efficacy when added to antipsychotics, though results are heterogeneous. Immunomodulatory strategies, including monoclonal antibodies targeting IL‑17, are currently under investigation in early‑phase trials. It is crucial to differentiate between primary immune dysregulation and secondary inflammation resulting from lifestyle factors. Longitudinal cohort studies that track immune markers from adolescence through adulthood will be instrumental in untangling causality. Animal models that recapitulate both neurobehavioral deficits and autoimmune pathology provide valuable mechanistic insights. Nevertheless, we must remain cautious about over‑generalizing findings across diverse patient populations. Future research should prioritize personalized medicine approaches, leveraging biomarkers to identify those who may benefit most from immune‑targeted therapies. Lastly, interdisciplinary collaboration among psychiatrists, immunologists, and geneticists will accelerate the translation of these discoveries into clinical practice.
Kylie Holmes
Let’s keep pushing for clinical trials that test anti‑inflammatory agents in early psychosis!
Jennifer Wees-Schkade
For anyone looking deeper, check out the meta‑analysis by Zheng et al., 2023; it breaks down CRP levels across diagnostic groups.
Fr. Chuck Bradley
Wow, that sounds like a breakthrough-maybe the next big headline!
Patrick Rauls
Yo, the whole thing is kinda wild lol but hey, if NSAIDs help, why not give it a shot? 😂
Angela Marie Hessenius
When we consider the historical evolution of psychiatric nosology, it becomes evident that the mind‑body dichotomy has long been a construct of Western epistemology. In many non‑Western traditions, mental disturbances have been interpreted through the lens of humoral imbalances, which in a modern sense mirrors the concept of systemic inflammation. Contemporary research, however, provides empirical scaffolding for these ancient notions by demonstrating that cytokine dysregulation can alter synaptic plasticity and neurotransmitter turnover. This convergence of old and new paradigms underscores the necessity of a culturally informed discourse on treatment, especially as we observe that dietary anti‑inflammatory patterns prevalent in Mediterranean and certain Asian cuisines correlate with lower incidence of both autoimmune and psychiatric disorders. Moreover, patient narratives from diverse backgrounds consistently highlight the psychosocial stressors that potentiate immune activation, reinforcing the biopsychosocial model. It is therefore incumbent upon clinicians to adopt an integrative approach that respects cultural dietary practices while employing evidence‑based pharmacotherapy. In doing so, we not only address the biological substrate but also honor the lived experience of patients across the globe. Such a holistic strategy promises to ameliorate symptom burden and improve quality of life, transcending the limitations of a purely reductionist framework.
Julian Macintyre
In summation, the extant literature mandates rigorous, double‑blind investigations to substantiate the therapeutic viability of immunomodulation in psychotic disorders.